Along with NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants, we also provide Notes and Lesson Plan for better understanding. Practice your concepts with NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants and Extra Questions. Shine among your friends after scoring high in Quiz and Worksheet.
Read more: Ncert solutions for class 7 science Wastewater Story
Table of Contents
Notes For NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants
(Also find NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants given below)
The production of new individuals from their parents is known as reproduction.
Modes Of Reproduction
- Roots, stems and leaves are called vegetative parts of plant.
- After a certain period of growth, most plants bear flowers.
- Flowers give rise to fruits.
- Fruits have seeds which germinate and form new plants.
- Flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant. A flower may have either the male part or the female part or both male and female parts.
- Two ways by which plants reproduce their offspring are:
- Asexual Reproduction – In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds or spores.
- Sexual Reproduction – In sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds.
Asexual Reproduction
Vegetative Propagation
- It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds.
- Since, reproduction is through the vegetative parts of the plant, it is known as vegetative propagation.
By Nodes
- Node: A node is a part of the stem/branch at which a leaf arises.
- Cut a branch with a node and bury the cutting in the soil. Upon growing, you’ll notice a new plant growing.
- Plants which grow by this method: Rose and Champa.

By Buds
- Flower buds develop into flowers.
- There are buds in the axil of leaves which develop into
- shoots. These buds are called vegetative buds.
- Axil: Point of attachment of the leaf at the node.
- A bud consists of a short stem around which immature overlapping leaves are folded.
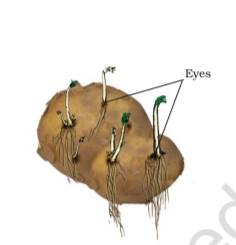
- Cut a piece of potato with an eye (which has buds) and bury in soil. Let it grow and observe the new plant.
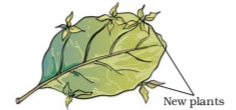
- Bryophyllum has buds in the margins of leaves. If a leaf of this plant falls on a moist soil, each bud can give rise to a new plant.
- Plants which grow by this method: Potato, Ginger, Turmeric, Bryophyllum.
By Roots
- Roots of some plants can also give rise to new plants.
- Plants which grow by this method: Sweet Potato and Dahlia.
By Detached Parts
- Some plants produce new plants when their parts get detached from the main plant body.
- Each detached part can grow into a new plant.
- Plants which grow by this method: Cactus
Advantages of Vegetative Propagation
- Plants produced by vegetative propagation take less time to grow.
- They bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
- The new plants are exact copies of the parent plant, as they are produced from a single parent.
Budding
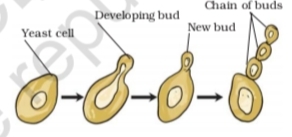
- Plant which grow by this method: Yeast, which is a microscopic single-celled organism.
- Yeast cells grow and multiply every few hours if sufficient nutrients are made available to them.
- The small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is called a bud.
- The bud gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms a new yeast cell.
- The new yeast cell grows, matures and produces more yeast cells.
- Sometimes, another bud arises from the bud forming a chain of buds. If this process continues, a large number of yeast cells are produced in a short time.
Fragmentation
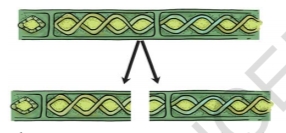
- In Fragmentation, the plant breaks up into two or more fragments. These fragments or pieces grow into new individuals.
- Plant which grows by this method: Algae. By the process of continued fragmentation, algae cover large area of ponds in short period of time.
Spore Formation
- Spores are asexual reproductive bodies.
- Each spore is covered by a hard protective coat to withstand unfavourable conditions such as high temperature and low humidity. So they can survive for a long time.
- When spores are released they keep floating in the air. As they are very light they can cover long distances.
- Under favourable conditions, a spore germinates and develops into a new individual.
- Plants which grow by this method: Fungi, Moss and Ferns.
Sexual Reproduction
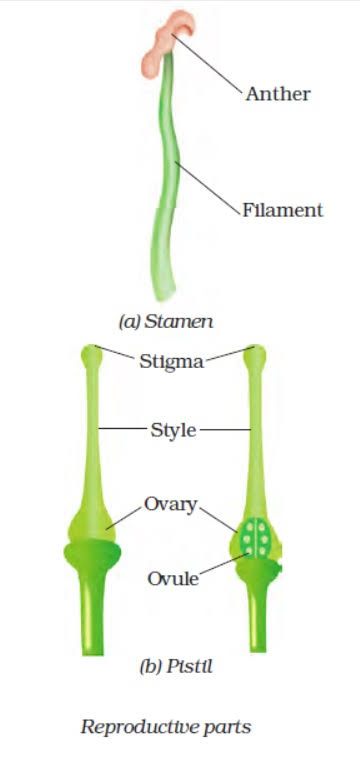
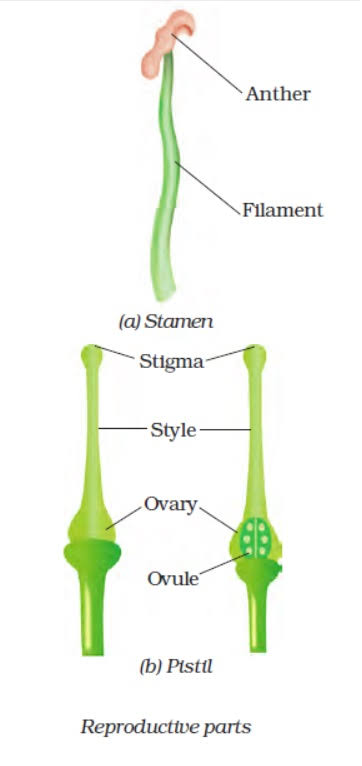
- The flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant. The stamens are the male reproductive part and the pistil is the female reproductive part.
- The flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamens are called unisexual flowers. Eg, Corn, Papaya and Cucumber.
- The flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual flowers. Eg, Mustard, Rose and Petunia.
- Both the male and the female unisexual flowers may be present in the same plant or in different plants.
- Anther contains pollen grains which produce male gametes (sex cells).
- A pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules. The female gamete or the egg is formed in an ovule.
- In sexual reproduction, a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote.
Pollination
- Pollen grains have a tough protective coat which prevents them from drying up.
- They are light and can be carried by wind or water.
- The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination.
- If the pollen lands on the stigma of the same flower it is called self-pollination.
- When the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of another flower of the same plant, or that of a different plant of the same kind, it is called cross-pollination.
- Pollination is aided by insects who carry pollen with them.

Fertilisation
- The process of fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilisation.
- This leads to formation of zygote.
- The zygote develops into an embryo.
Fruits And Seed Formation
After fertilization,
- Ovary grows into fruit. Fruit is the ripened ovary.
- Some fruits are fleshy and juicy like mango, orange and apple.
- Some fruits are hard like almonds and walnuts.
- Ovules develops into seeds. A seed consist of an embryo in a protective seed coat.
- Other parts of the flower, fall off.
Seed Dispersal
- Plants benefit by seed dispersal.
- It prevents competition between the plant and its own seedlings for sunlight, water and minerals.
- It also enables the plants to invade new habitats for wider distribution.
- By Wind
- Winged Seeds of maple and drumsticks.
- Light seeds of grass.
- Hairy seeds of aak.
- Hairy fruit of sunflower.
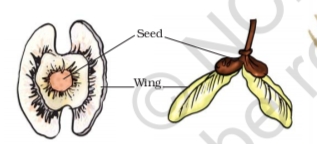
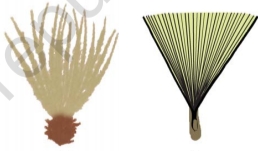
- By Water
These fruits or seeds usually develop floating ability in the form of spongy or fibrous outer coat as in coconut.
- By Animals
Spiny seeds with hooks get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant places by them. Eg, Xanthium and Urena.

- By Bursting
When the fruits burst with sudden jerk, the seeds are scattered far from the parent plants. Eg, Castor and Balsam.
NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants
(Also find NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants Extra Questions given below)
Q. 1. Fill in the blanks:
- Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called …………….
- A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called …………….
- The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as ……………..
- The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as …………….
- Seed dispersal takes place by means of …………… and ………..
A)
- Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called vegetative propagation.
- A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called unisexual flower.
- The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as pollination.
- The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as fertilization.
- Seed dispersal takes place by means of wind and water.
Q. 2. Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
A) Different methods of asexual reproduction are:
Vegetative Propagation: It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds. Since, reproduction is through the vegetative parts of the plant, it is known as vegetative propagation.
- By Nodes: Anode is a part of the stem/branch at which a leaf arises. Cut a branch with a node and bury the cutting in the soil. Upon growing, you’ll notice a new plant growing. Plants which grow by this method: Rose and Champa
- By Buds: Flower buds develop into flowers. There are buds in the axil of leaves which develop into shoots. These buds are called vegetative buds. Axil: Point of attachment of the leaf at the node. A bud consists of a short stem around which immature overlapping leaves are folded. Cut a piece of potata with an eye ( which has buds) and bury in soil. Let it grow and observe the new plant. Bryophyllum has buds in the margins of leaves. If a leaf of this plant falls on a moist soil, each bud can give rise to a new plant. Plants which grow by this method: Potato, Ginger, Turmeric, Bryophyllum.
- By Roots: Roots of some plants can also give rise to new plants. Plants which grow by this method: Sweet Potato and Dahlia.
- By Detached Parts: Some plants produce new plants when their parts get detached from the main plant body. Each detached part can grow into a new plant. Plants which grow by this method: Cactus
Budding: Plant which grow by this method: Yeast, which is a microscopic single-celled organism. Yeast cells grow and multiply every few hours if sufficient nutrients are made available to them. The small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is called
a bud. The bud gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms a new yeast cell. The new yeast cell grows, matures and produces more yeast cells. Sometimes, another bud arises from the bud forming a chain of buds. If this process continues, a large number of yeast cells are produced in a short time.
Fragmentation: In Fragmentation, the plant breaks up into
two or more fragments. These fragments or pieces grow into new individuals. Plant which grows by this method: Algae. By the process of continued fragmentation, algae cover large area of ponds in short period of time.
Spore Formation: Spores are asexual reproductive
bodies. Each spore is covered by a hard protective coat to withstand unfavourable conditions such as high temperature and low humidity. So they can survive for a long time. When spores are released they keep floating in the air. As they are very light they can cover long distances. Under favourable conditions, a spore germinates and develops into a new individual. Plants which grow by this method: Fungi, Moss and Ferns.
Q. 3. Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
A)
- When two parents are involved in the process of reproduction, it is called sexual reproduction.
- It requires seeds.
- Male gamete and female gamete fuse to form a zygote.
- Offsprings inherit the characteristics of both the parents.
Q. 4. State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
A)
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds or spores. | In sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds. |
Q. 5. Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
A)
Q.6.Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination
A)
| Self Pollination | Cross Pollination |
| If the pollen lands on the stigma of the same flower it is called self-pollination. | When the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of another flower of the same plant, or that of a different plant of the same kind, it is called cross-pollination. |
| Eg, wheat, peas etc. | Eg, lady-finger, tomato and brinjal etc. |
Q. 7. How does the process of fertilization take place in flowers?
A) Anther contains pollen grains which produce male gametes (sex cells). A pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules. The female gamete or the egg is formed in an ovule. The process of fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilisation.
Q. 8. Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
A) Following are the ways in which the seeds are dispersed:
- By Wind
- Winged Seeds of maple and drumsticks.
- Light seeds of grass.
- Hairy seeds of aak.
- Hairy fruit of sunflower.
- By Water
These fruits or seeds usually develop floating ability in the form of spongy or fibrous outer coat as in coconut. - By Animals
Spiny seeds with hooks get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant places by them. Eg, Xanthium and Urena. - By Bursting
When the fruits burst with sudden jerk, the seeds are scattered far from the parent plants. Eg, Castor and Balsam.
Q. 9. Match items in Column I with those in Column II
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Bud | (i) Maple |
| (b) Eyes | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (c) Fragmentation | (iii) Yeast |
| (d) Wings | (iv) Bread Mould |
| (e) Spores | (v) Potato |
| (vi) Ross |
A)
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Bud | (iii) Yeast |
| (b) Eyes | (v) Potato |
| (c) Fragmentation | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (d) Wings | (i) Maple |
| (e) Spores | (iv) Bread Mould |
Q. 10. Tick the correct answer:
- The reproductive part of a plant is the:
1. Leaf
2. Stem
3. Root
4. Flower
A) (1) Flower
- The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called:
1. Fertilisation
2. Pollination
3. Reproduction
4. Seed formation
A) (1) Fertilisation
- Mature ovary forms the:
1. Seed
2. Stamen
3. Pistil
4. Fruit
A) (4) Fruit
- A spore producing plant is:
1. Rose
2. Bread mould
3. Potato
4. Ginger
A) (2) Bread mould
- Bryophyllum can be reproduced by its:
1. Stem
2. Leaves
3. Roots
4. Flower
A) (2) Leaves
Practice Last Year Question Papers
Some Frequently Asked Questions
(Here you can find the NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants FAQs.)
Q. 1. What do you think will happen if all seeds of a plant were to fall at the same place and grow there?
A) There would be severe competition for sunlight, water, minerals and space. As a result the seeds would not grow into healthy plants. Some may either die.
Q. 2. Why flowers are generally so colourful and fragrant?
A) Flowers are colourful and fragnant to attract insects so that they suck nectar and pollen grains stick to their body which will help in pollination.
Q. 3. How the male gamete in the pollen grain reaches the female gamete present in the ovule?
A) A pollen grain on the stigma grows a tiny tube which travels to the style which leads to ovary. This tube carries a male gamete to meet a female gamete in an ovule and process of fertilization takes place.
Conclusion: NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants
Above written includes NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Animals, detailed Explanation, and Question Answers. Browse our site for various detailed and easy NCERT Solutions and CBSE Notes.





