NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms, here we are going to give you a summary of NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms with class 7 science chapter 10 question answer from the textbook. In this chapter, we will study the meaning of respiration and the different respiration in different organisms. Your all doubts from the chapter NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms will be cleared from this. Breathing is a part of respiration. Let us learn about respiration.
Read more: NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Light
Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms: Introduction
The food has stored energy, which is released during respiration. Respiration is important because it gives our body energy which is used to do important tasks like nutrition, transport, excretion, and reproduction. Therefore, all living organisms respire to get energy from food. The oxygen that we breathe in is important because it helps in the breakdown of food which releases energy in our body. The process of breakdown of food in the cell with the release of energy is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all organisms.
Different types of respiration.
- Aerobic respiration: Food is broken down into carbon dioxide and water using oxygen is called aerobic respiration.
- Anaerobic respiration: Food is broken down into carbon dioxide and water without using oxygen is called anaerobic respiration.
Breakdown of food releases energy.
Glucose (With the use of oxygen ) → carbon dioxide + water + energy
Anaerobes: Organisms that can survive in the absence of air are called anaerobes, eg. yeast. They use anaerobic respiration to get energy.
In the absence of oxygen, glucose breaks down into alcohol and carbon dioxide as given below:
Glucose (Without the use of oxygen) → alcohol + carbon dioxide + energy
NOTE: Yeasts are single-celled organisms. They respire anaerobically and during this process yield alcohol. They are, therefore, used to make wine and beer.
Anaerobic respiration in our muscles
Anaerobic respiration also happens in our muscles but only for a short time, when there is a temporary lack of oxygen in situations like long hours of heavy exercise, fast running, cycling, walking for many hours or heavy weight lifting. This is because in these situations demand energy is high. But the supply of oxygen to produce the energy is limited. Thus anaerobic respiration takes place.
Glucose(in muscle) (in the absence of oxygen) → lactic acid + energy
Due to this anaerobic respiration in our muscles, cramps occur.
The partial breakdown of glucose produces lactic acid. Accumulation of this lactic acid causes muscle cramps. Hot water bath or massage improves the circulation of blood and the supply of oxygen to the muscle cells increases. The increase in the supply of oxygen results in the complete breakdown of lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water and thus we get relief from muscle cramps after a hot massage.
BREATHING
Let us perform an activity to understand breathing deeply.
ACTIVITY 1 – NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Let us close our nostrils and mouth tightly and look at a watch.
- What did you feel after some time? How long were you able to keep both of them closed?
- Note down the time for which you could hold your breath
At most it is 30 seconds and up to 2 minutes
We know that we cannot survive for long without breathing.
Breathing means taking in air rich in oxygen and giving out air rich in carbon dioxide with the help of respiratory organs.
Inhalation is taking in of air rich in oxygen into the body
Exhalation is giving out of air rich in carbon dioxide
It is a continuous process all the time and throughout the life of an organism.
Breathing rate: number of times a person breathes in a minute
During breathing inhalation and exhalation take place alternately.
Let us find out if breathing is constant or it changes according to the requirement of oxygen by the body
ACTIVITY 2 – NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Generally we are not aware that we are breathing.
- However, if you try you can count your rate of breathing.
- Breathe in and out normally.
- Let us find out how many times we breathe in and breathe out in a minute?
- Did you inhale the same number of times as you exhaled?
Now count your breathing rate (number of breaths/minute) after brisk walk and after running. Record your breathing rate as soon as you finish and also after complete rest.
Observation: We realise that whenever a person needs extra energy, he/she breathes faster. As a result more oxygen is supplied to our cells. It speeds up the breakdown of food and more energy is released.
Activity 3 – NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
Can we say in which activity, the rate of breathing will be the slowest and in which it will be the fastest? Let us assign numbers to the pictures in the order of increasing rate of breathing according to our experience.

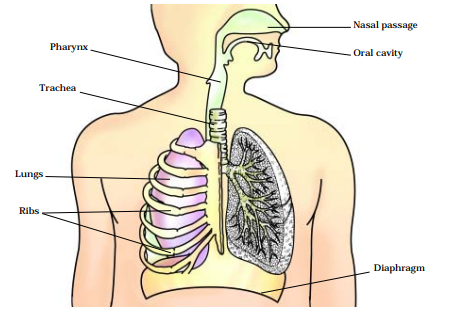
HOW DO WE BREATHE?
Let us now learn about the mechanism of breathing.
We take in air through our nostrils generally. we inhale air, it passes through our nostrils into the nasal cavity.
The air then reaches our lungs through the windpipe.
Lungs are present in the chest cavity (This cavity is surrounded by ribs on the sides.)
A large, muscular sheet called a diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity.
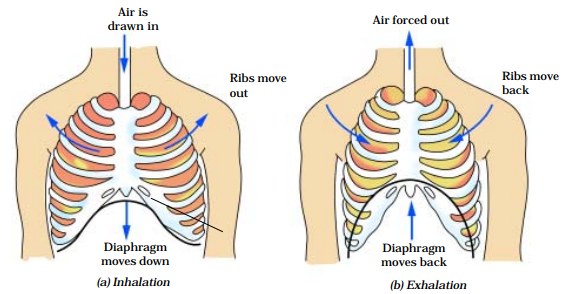
INHALATION
Breathing involves the movement of the diaphragm and the rib cage
ribs move up and outwards and the diaphragm moves down during inhalation.
This movement increases space in our chest cavity and air rushes into the lungs.
The lungs get filled with air.
EXHALATION
Ribs move down and inwards, while the diaphragm moves up to its former position.
This reduces the size of the chest cavity and air is pushed out of the lungs and air is exhaled.
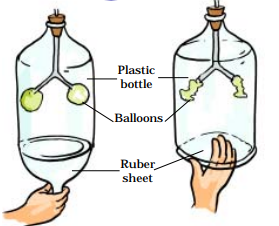
ACTIVITY 4 – NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Let us understand the mechanism of breathing by a simple model by class 7 science chapter 10 question answer.
- We take a wide plastic bottle. Let us remove the bottom and get a Y-shaped glass or plastic tube. We make a hole in the lid so that the tube may pass through it.
- To the forked end of the tube we fix two deflated balloons. We introduce the tube into the bottle as shown in. Now we cap the bottle, seal it to make it airtight. To the open base of the bottle we tie a thin rubber or plastic sheet using a large rubber band.
- We pull the rubber sheet from the base downwards and watch the balloons.
- Next, we push the rubber/plastic sheet up and observe the balloons.
Did you see any changes in the balloons?
Ans. Yes, we see changes in the balloons.
What do the balloons in this model represent?
Ans. Lungs
What does the rubber sheet represent?
Ans. Diaphragm
WHAT DO WE BREATHE OUT?
Let us see what we breathe out with an activity.
Activity 5 – NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- We take a slender, clean test tube or a glass/plastic bottle.
- We make a hole in its lid and fix it on the bottle and pour some freshly prepared lime water in the test tube.
- Let us insert a plastic straw through the hole in the lid in such a way that it dips in lime water. Now we blow gently through the straw a few times.
Is there a change in the appearance of lime water?
Ans. Yes
What do we exhale?
Ans. We exhale carbon dioxide and a mixture of gases along with it.
BREATHING IN OTHER ANIMALS
Animals such as elephants, lions, cows, goats, frogs, lizards, snakes, birds, have lungs in their chest cavities like human beings.
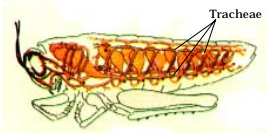
Cockroach: A cockroach has small openings on the sides of its body. Other insects also have similar openings. These openings are called spiracles. Insects have a network of air tubes called tracheae for gas exchange. Oxygen rich air rushes through spiracles into the tracheal tubes, diffuses into the body tissue, and reaches every cell of the body. Similarly, carbon dioxide from the cells goes into the tracheal tubes and moves out through spiracles. These air tubes or tracheae are found only in insects and not in any other group of animals.
Earthworm: Earthworms breathe through their skins. The skin of an earthworm feels moist and slimy on touching. Gases can easily pass through them. Though frogs have a pair of lungs like human beings, they can also breathe through their skin, which is moist and slippery.
BREATHING UNDER WATER : NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
Gills in fish help them to use oxygen dissolved in water. They are projections of the skin. The gills are well supplied with blood vessels for exchange of gases.
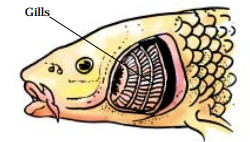
Respiration in organisms class 7
Cellular respiration occurs within the cells of all living organisms. Cells are the place where it is where food (glucose) can be broken in carbon dioxide as well as water by the use of oxygen. When glucose is broken down through the use of oxygen, it is known as aerobic respiration. The food can be also broken down without oxygen.
Respiration in Plants
Plants also take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. In the cells oxygen is used to break down glucose into carbon dioxide and water as in other organisms. In plants each part can independently take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. The leaves of the plants have tiny pores called stomata for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Like all other living cells of the plants, the root cells also need oxygen to generate energy. Roots take up air from the air spaces present between the soil particles
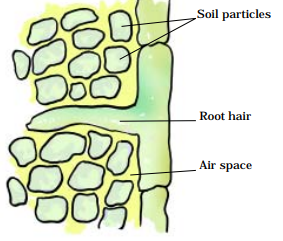
NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms : Conclusion
Respiration is essential for survival of living organisms. respiration in organisms class 7 extra questions with answers from this chapter states the process of releasing energy from the food. Respiration is a vital biological process. All living organisms need to respire to get the energy needed for their survival. Let us now do exercises from NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms and class 7 science chapter 10 question answer to understnad significance of this chapter.
NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms : Exercises
1. Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race?
Ans. An athlete needs a lot of energy running in a race, and thus a lot of energy needs to be released. So they need to respire faster and so they breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race.
2. List the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
| aerobic | anaerobic |
| Needs Oxygen | Doesn’t Need Oxygen |
| Carbon dioxide and water produced | Carbon dioxide and alcohol produced |
| Occurs in most multicellular organisms. | Occurs in most unicellular organisms and yeast. |
3. Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air?
Ans. The nasal tract has fine hairs which get triggered when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air thus we sneeze.
4. Take three test-tubes. Fill 3/4th of each with water. Label them A, B and C. Keep a snail in test-tube A, a water plant in test-tube B and in C, keep snail and plant both. Which test-tube would have the highest concentration of CO2?
Ans. Test tube A would have the highest concentration of CO2.
5. Tick the correct answer:
(a) In cockroaches, air enters the body through
(i) lungs
(ii) gills
(iii) spiracles
(iv) skin
Ans. (iii) spiracles
(b) During heavy exercise, we get cramps in the legs due to the accumulation of
i) carbon dioxide
(ii) lactic acid
(iii) alcohol
(iv) water
Ans. (ii) lactic acid
(c) Normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest is:
(i) 9-12
(ii) 15-18
(iii) 21-24
(iv) 30-33
Ans. (ii) 15-18
(d) During exhalation, the ribs
(i) move outwards
(ii) move downwards
(iii) move upwards
(iv) do not move at all
Ans. (ii) move downwards
Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Yeast | (i) Earthworm |
| (b) Diaphragm | (ii) Gills |
| (c) Skin | (iii) Alcohol |
| (d) Leaves | (iv) Chest cavity |
| (e) Fish | (v) Stomata |
| (f) Frog | (vi) Lungs and skin |
| (vii) Tracheae. |
Ans.
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Yeast | (iii) Alcohol |
| (b) Diaphragm | (iv) Chest cavity |
| (c) Skin | (i) Earthworm |
| (d) Leaves | (v) Stomata |
| (e) Fish | (ii) Gills |
| (f) Frog | (vi) Lungs and skin |
Mark T if the statement is true and F if it is false:
(i) During heavy exercise the breathing rate of a person slows down. (T/F)
Ans. False
(ii) Plants carry out photosynthesis only during the day and respiration only at night. (T/F)
Ans. False
(iii) Frogs breathe through their skins as well as their lungs. (T/F)
Ans. True
(iv) The fishes have lungs for respiration. (T/F)
Ans. False
(v) The size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation. (T/F)
Ans. True
Given below is a square of letters in which are hidden different words related to respiration in organisms. These words may be present in any direction ó upwards, downwards, or along the diagonals. Find the words for your respiratory system. Clues about those words are given below the square.
(i) The air tubes of insects
Ans. Trachea
(ii) Skeletal structures surrounding chest cavity
Ans. Ribs
(iii) Muscular floor of chest cavity
Ans. Diaphragm
(iv) Tiny pores on the surface of leaf
Ans. Stomata
(v) Small openings on the sides of the body of an insect
Ans. Spiracles
(vi) The respiratory organs of human beings
Ans. Lungs
(vii) The openings through which we inhale
Ans. Nostrils
(viii) An anaerobic organism
Ans. Yeast
(ix) An organism with a tracheal system
Ans. Ant
9. The mountaineers carry oxygen with them because:
(a) At an altitude of more than 5 km there is no air.
(b) The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
(c) The temperature of air is higher than that on the ground.
(d) The pressure of air is higher than that on the ground.
Ans. (b) The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
FAQ : NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
Why do we sneeze when we inhale dust laden air ?
The openings through which we inhale ?
Our noses are the part of our body that allows us to breathe air or inhale it.





