Along with NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource, we also provide Notes and Lesson Plan made specially by our Study Rankers for better understanding. Students may read the NCERT Science Chapter 16 PDF to practice concepts with NCERT Solutions and Extra Questions and Answers by keeping in mind the latest CBSE curriculum. Shine among your friends after scoring high in Quiz, MCQ and Worksheet.
Read more: Ncert solutions for class 7 science Transportation in Animals and Plants
Table of Contents
Notes For NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
(Also find NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource given below)
- We celebrate World Water day 22 March! We celebrate water day every year to attract the attention of everybody towards the importance of conserving water.
- The amount of water recommended by the United Nations for drinking, washing, cooking and maintaining proper hygiene is a minimum of 50 litres per person per day.
- The International Year of Freshwater was year 2003 to make people aware of this dwindling natural resource.

How much Precious Water Is Available
- Water covers 71% of the earth’s surface.
- Seas and oceans, rivers, lakes, ice caps, as groundwater and in the atmosphere contain all the water present on the earth.
- For direct human consumption, most of this water is not fit.
- Only freshwater is fit for use which is roughly 0.006% of all water found on the earth.
Forms of Water
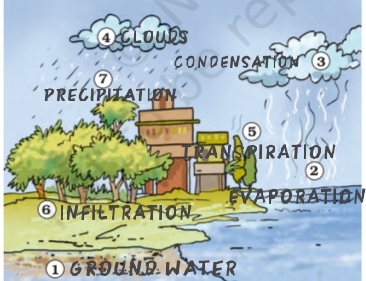
- Water on the earth has been maintained for millions of years by various processes which make the Water Cycle
- When water circulates through the water cycle it is present in all the three forms, i.e., solid, liquid and gas.
- The solid form, snow and ice, is present as ice caps at the poles of the earth, snow-covered mountains and glaciers.
- Liquid water is present in oceans, lakes, rivers, and even underground.
- The gaseous form is the water vapour present in the air around us.
- The continuous cycling of water among its three forms keeps the total amount of water on the earth constant even when the whole world is using it.
- Civic Bodies maintain the water supply system in most towns and cities. It draws water from nearby lakes, rivers, ponds or wells. A network of pipes supply water.
- Many villages do not have such a water supply system. There, people fetch water directly from the sources. Often people and even children have to walk several kilometres to fetch water.
- A large number of people draw water from wells, tube wells or hand pumps.
Groundwater as an Important Source of Water
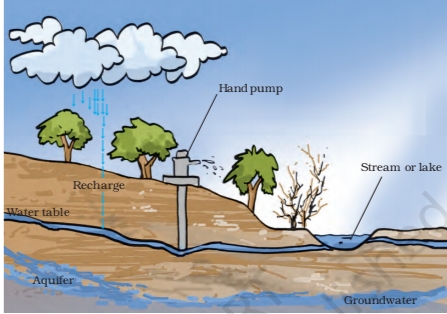
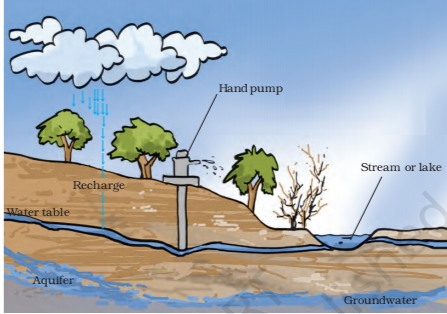
- Water Table is the level above which water fills all the space between particles of soil and gaps between rocks.
- The water table may be at a depth of less than a metre or may be several metres below the ground.
- Groundwater is the water below the water table.
- The rainwater and water from other sources such as rivers and ponds seeps through the soil and fills the empty spaces and cracks deep below the ground.
- Infiltration is the process of seeping of water into the ground. Infiltration recharges the groundwater.
- Layers of hard rock stores groundwater between them. This is an aquifer. Tube wells or handpumps can pump out the water present in aquifers.
Depletion of Water Table
- If we draw as much water as natural processes repleneshes, it will not affect the groundwater.
- This may happen due to many reasons. Increase in population, industrial and agricultural activities are some common factors affecting water table.
- Scanty rainfall is another factor that may deplete the water table.
- Yet another factor affecting water table could be deforestation and decrease in the effective area for seepage of water.
Increasing Population
- Increasing population creates demand for construction of houses, shops,offices, roads and pavements.
- This decreases the open areas like parks, and playgrounds.
- This, in turn, decreases the seepage of rainwater into the ground.
- Moreover a huge amount of water is required for construction work. Often groundwater is used for this purpose.
- On the one hand we are consuming more groundwater, and on the other we are allowing lesser water to seep into the ground. This results in depletion of water table.
Increasing Industries
- All the industries use water. For almost everything that we use, needs water somewhere in its production process.
- These industries draw water from the ground.
Agricultural Activities
- A majority of farmers in India depend upon rains for irrigating their crops.
- Irrigation systems such as canals are there only in a few places.
- Therefore, farmers have to use groundwater for irrigation.
- Population pressure on agriculture forces increasing use of groundwater day by day.
- This results in depletion of water table.
Distribution of Water
- The distribution of water over the globe is quite uneven due to a number of factors.
- Some places have good amount of rain and are water-rich. On the other
- hand, there are deserts which have scanty rainfall.
- India is a vast country and the rainfall is not the same everywhere.
- Some regions have excessive rains while some others have very little rainfall.
- Excessive rains cause floods, whereas the absence of rains results in droughts.
- Therefore, some regions in our country may have floods while others may suffer from droughts at the same time.
Water Management
Sources of Water Wastage
- Individuals waste water while brushing teeth, shaving, bathing, washing and during many other activities.
- Leaking taps is another source of huge water wastage.
- Water supply pipes leaking and a lot of water gushing out of the pipes.
- Rainfall flowing away is a waste of precious natural resource.
Various Water Harvesting Systems
- The rainwater can be used to recharge the groundwater. This is referred to as water harvesting or rainwater harvesting.
- An age old practice of water storage and water recharge are the bawris. You may have learnt about bawris in History Chapter 5
- Bawri was the traditional way of collecting water.
- With time, the bawris fell into disuse and garbage started piling in these reservoirs.
- However, the bawris are being revived.
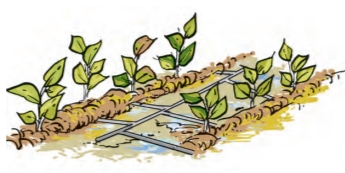
- Drip irrigation is a technique of watering plants by making use of narrow tubings which deliver water directly at the base of the plant.
What Role Can You Play?
- Never leave the tap running when not in use.
- Try to use bucket and mug while bathing.
- Mop the floor instead of washing.
- Try to reuse water.
- Practice water harvesting.
Effects of Water Scarcity On Plants
- Plants need water to get nutrients from the soil to prepare their food.
- A world without plants shall mean no food, no oxygen, not enough rain, and innumerable other problems.
NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
(Also find NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water: An Important Resource FAQs given below)
Q. 1. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
- The freshwater stored in the ground is much more than that present in the rivers and lakes of the world. (T/F)
- Water shortage is a problem faced only by people living in rural areas. (T/F)
- Water from rivers is the only source for irrigation in the fields. (T/F)
- Rain is the ultimate source of water. (T/F)
A)
- The freshwater stored in the ground is much more than that present in the rivers and lakes of the world. TRUE
- Water shortage is a problem faced only by people living in rural areas. FALSE
- Water from rivers is the only source for irrigation in the fields. FALSE
- Rain is the ultimate source of water. TRUE
Q. 2. Explain how groundwater is recharged.
A) The rainwater and water from other sources such as rivers and ponds seeps through the soil and fills the empty spaces and cracks deep below the ground. This process of seeping of water into the ground is called infiltration. Infiltration recharges the groundwater.
Q. 3. There are ten tubewells in a lane of fifty houses. What could be the long-term impact on the water table?
A) According to the question, about 5 families will use one tubewell. Water table will not be affected if the replenishment of water is equal to the usage of water. If there’s shortage of rainfall, then the depletion of groundwater might take place.
Q. 4. You have been asked to maintain a garden. How will you minimise the use of water?
A)
I will use the following techniques to minimise the use of water in my garden:
- Reuse water.
- Practice rainwater harvesting.
- Practice drip irrigation.
Q. 5. Explain the factors responsible for the depletion of water table.
- Depletion of groundwater may happen due to many reasons. Increase in population, industrial and agricultural activities, scanty rainfall and deforestation are some common factors affecting water table.
- Increasing Population
- It creates demand for construction of houses, shops,offices, roads and pavements.
- This decreases the open areas like parks, and playgrounds, which decreases the seepage of rainwater into the ground.
- Also, groundwater is used for these constructions.
- This results in depletion of water table.
- Industrial Activities
- Industries draw water from the ground for using it in the process of making our daily goods.
- Agricultural Activities
- Maximum number of farmers have to use groundwater for irrigation.
- Population pressure on agriculture forces increasing use of groundwater day by day.
- This results in depletion of water table.
Q. 6. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate answers:
- People obtain groundwater through …………….. and ……………
- Three forms of water are solid, …………. and …………….
- The water bearing layer of the earth is …………….
- The process of water seepage into the ground is called …………….
A)
- People obtain groundwater through tube wells and handpumps.
- Three forms of water are solid, liquid and gas.
- The water bearing layer of the earth is aquifer
- The process of water seepage into the ground is called infiltration.
Q. 7. Which one of the following is not responsible for water shortage?
- Rapid growth of industries
- Increasing population
- Heavy rainfall
- Mismanagement of water resources
A) 3. Heavy rainfall
Q. 8. Choose the correct option. The total water:
- In the lakes and rivers of the world remains constant.
- Under the ground remains constant.
- In the seas’and oceans of the world remains constant.
- Of the world remains constant.
A) 4. Of the world remains constant.
Q.9.Make a sketch showing groundwater and water table. Label it.
Some Frequently Asked Questions
(Here you can find the NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource FAQs.)
Q. 1. Why do some parts of our country suffer from flood while at the same time some parts suffer from draught?
A)
- The distribution of water over the globe is quite uneven due to a number of factors.
- Some places have good amount of rain and are water-rich. On the other hand, there are deserts which have scanty rainfall.
- Excessive rains cause floods, whereas the absence of rains results in droughts.
- Therefore, some regions in our country may have floods while others may suffer from droughts at the same time.
Q. 2. The earth’s surface is covered by 71% of water. Still, huge population face water shortage. Comment.
A) Out of all the water on earth’s surface, only freshwater is fit for use which is roughly 0.006% of all water found on the earth. Therefore, a huge population suffer from water shortage.
Conclusion: NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
Above written includes NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource, detailed Explanation, and Question Answers. Browse our site for various detailed and easy NCERT Solutions and CBSE Notes.





