NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants, here we are going to give you a summary of this chapter along with notes which may be referred to during the examination time in order to revise the chapter in short time duration. In this chapter, we will study how plants reproduce.
Table of Contents
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants: Introduction
You may have thought sometimes that whether all plants grow through seeds or not. The answer to that question has been discussed in detail further. All living things, including both plants and animals, have the capacity to create offspring at some point in their existence. The process of creating a new organism from an existing organism (or the parent) within the same species is called reproduction. This process is important as it ensures the continuity of life on Earth.
Also, refer to NCERT solutions for class 7 science chapter 3 Fiber to Fabric

NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants: Summary
- Plants reproduce by two modes, which are sexual and asexual reproduction.
- There are several methods of asexual reproduction such as fragmentation, budding, spore formation and vegetative propagation.
- Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes.
- Flower is the reproductive part of a plant.
- There are two types of flowers, namely: Uni-sexual and Bisexual.
- A uni-sexual flower has either the male or the female reproductive part.
- A bisexual flower has both male and female reproductive parts.
- The male gametes are found inside the pollen grains and female gametes are found in the ovule.
- The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilization.
- Fertilized egg is called zygote.
- The zygote develops into an embryo.
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants: Notes
Reproduction
The process of creating a new organism from an existing organism (or the parent) within the same species is called reproduction. In plants, flowers are the reproductive parts whereas the roots, stems and leaves of the plants are considered as vegetative parts of a plant.
There are two modes of reproduction: Asexual reproduction and Sexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which only one parent produces a child. The offspring is physically and genetically identical to its parent.
There are four types of asexual reproduction:
- Vegetative propagation
- Budding
- Fragmentation
- Spore formation
These are discussed below.
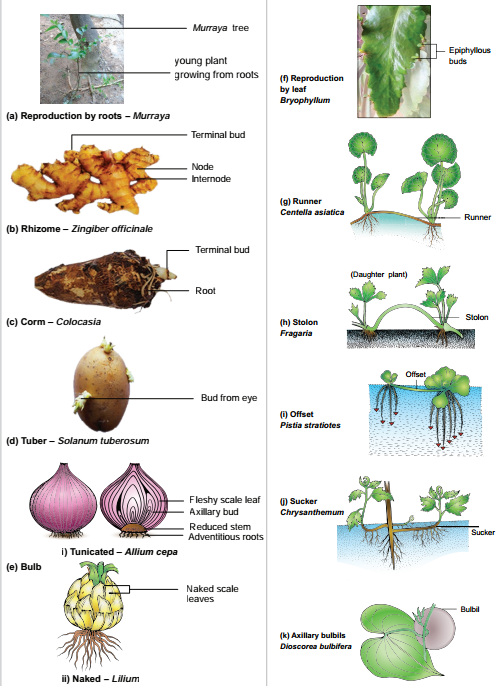
(1) Vegetative Propagation
It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds. Since reproduction is done here through the vegetative parts of the plant, it is known as vegetative propagation. Eg: Bryophyllum
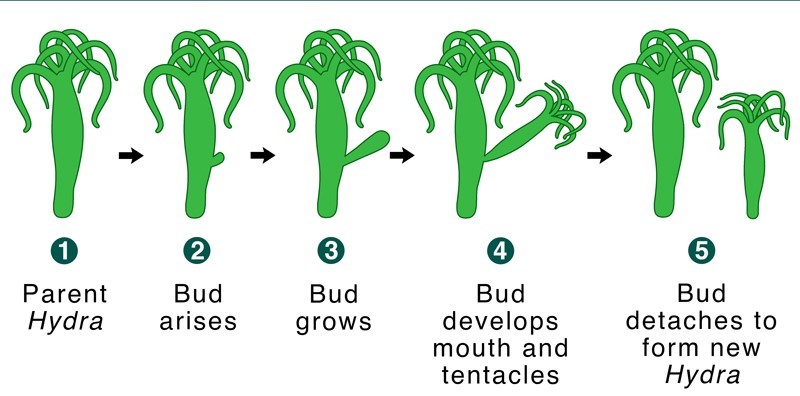
(2) Budding
The act of developing an individual from the buds that form on the parent body is known as budding. The parent organism provides the bud with food and protection .The bud separates from the parent when it is completely formed. Eg: Hydra
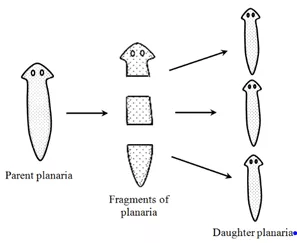
(3) Fragmentation
In this type of reproduction, each fragment that separates from the parent body grows into a new individual. Eg: Planaria
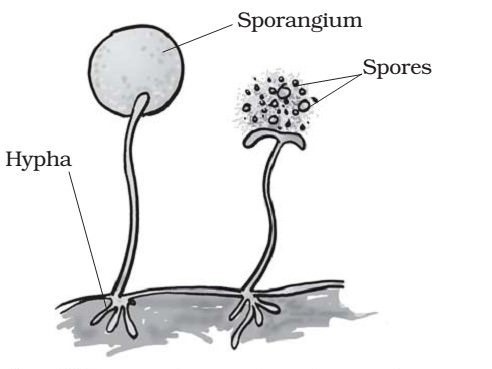
(4) Spore Formation
Some organism tend to form a sac-like structure known as spore for reproduction. Each spore has a tough protective coating to withstand unfavorable environmental conditions like high temperatures and low humidity. In the right circumstances, a spore germinates and grows into a new individual. Eg: Fungus
Sexual Reproduction
The flower is the reproductive part of the plant. The gametes that are responsible for reproduction are produced by flowers. Gametes fuse together during sexual reproduction in plants, creating seeds that eventually grow into new plants.
Pollen grains are the male gamete while ovule is the female gamete. Pollen grains are produced by anthers while ovule is produced by pistils.
When the pollen grains are transferred from the male reproductive part to the female part of the flower, it is called pollination.
- There are two types of flowers:
- Uni-sexual- A uni-sexual flower has either the male or the female reproductive part.
- Bisexual- A bisexual flower has both male and female reproductive parts.
In sexual reproduction, both the male (pollen grains) and female (ovule) gametes fuse together to form a zygote. This fusion is known as fertilization and the new cell formed out of the fusion is called zygote. The zygote then transforms into an embryo.
Also refer to NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants detailed explanation
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants: PDF Download
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants: Conclusion
In conclusion, we learned a lot about NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants. As a result, we can easily differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in detail and can also answer the question that how do plants reproduce. NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants notes have been made by our subject matter experts and have been explained in the simplest way possible along with examples.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs) on NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
List some features of sexual reproduction.
(1) Two parents are involved
(2) Variation is present in same species
(3) The parent and offspring isn’t identical
(4) Fertilization takes place
(5) Is a slow and lengthy process as compared to asexual reproduction.
List some features of asexual reproduction.
(1) Only one parent is involved
(2) The offspring is genetically similar
(3) The parent and offspring are identical
(4) Fertilization does not take place
(5) It is a rapid process.
Draw a sketch of a flower and label it.
The pistil bears the ovule (female gamete)
What are the agents of pollination?
What are the types of pollination?
(1)When the pollen grains tends to land on the stigma of the same flower or lands on a different flower but of the same plant, it is called self pollination.
(2)When the pollen grains land on the stigma of a different plant of same kind, it is called cross pollination.





